What is it?
2-factor authentication (also known as two-step authentication and 2FA) is a means of making online accounts more secure by using more than one method of authentication. Typically, this involves using a traditional password with the addition of a code that is supplied via a dedicated app.
Why do I need it?
With hackers becoming more sophisticated and data breaches occurring on a daily basis, passwords alone can no longer be trusted as a means of securing your online accounts.
Using a second means of authentication makes it much more difficult for hackers to guess your password or opportunistic criminals to use your it has been leaked online.
While it may seem like a lot to do every time you login to a website, it quickly becomes habit.
How do I use it?
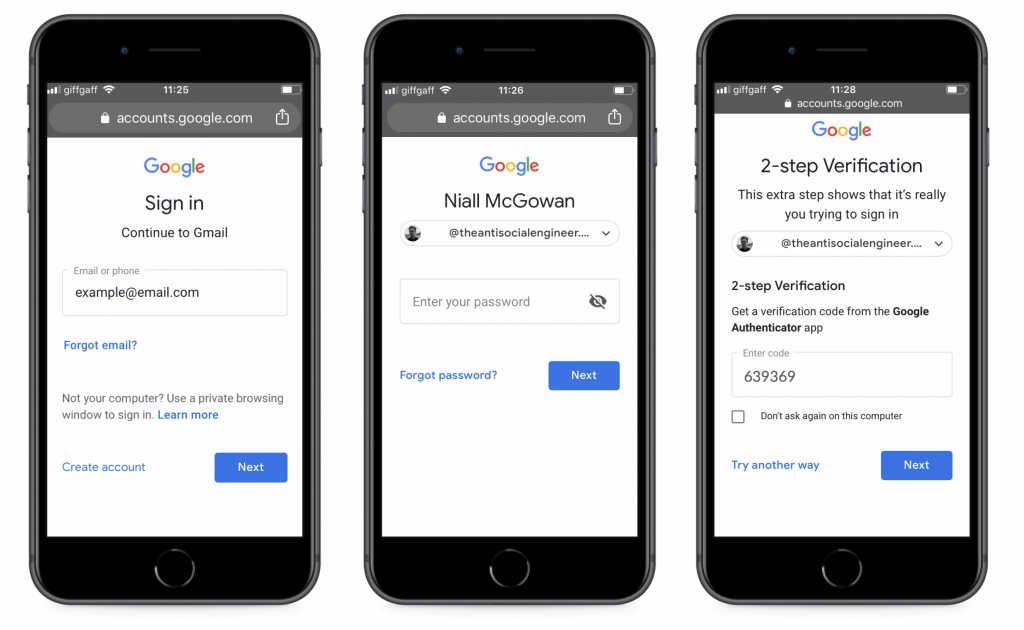
To use 2-factor authentication first you need an app. There are several apps available, offering different options, find a list of options at the end of this article. Second, you need to activate the 2-factor authentication service on the account you need it on. Typically, this involves the following:
- Going to the ‘account settings’ setting on the account in question
- Going to the security or advanced security page or tab
- Clicking on activate 2 factor authentication
- Using your selected 2 factor authentication app to scan the QR code generated by the website
- Entering the 2 factor authentication code for the first time
After this, whenever you use your password to sign into that account – you will be prompted to enter your 2 factor code. For more specific instructions for a large array of online services including social media sites, Amazon, and Google visit turnon2fa. Some 2 factor authentication apps offer an alternative to entering the code. Instead of generating a code, when you sign on to your account, the app will send a prompt to your phone. This prompt just asks if you had attempted to sign in. If yes is selected, you are signed into the account. While you still have to use a phone to authenticate, this does save time in terms of opening the app and typing the code into the website in question.
What apps are available?
Google Authenticator – a simple app and the most commonly used. Google also offers a prompt to authenticate service, however, this needs to be activated separately and only works for Google accounts.
Microsoft Authenticator – Microsoft’s take on 2-factor authentication. This app has a built in prompt to authenticate service for Microsoft accounts making in particularly useful for enterprise and Office365 based accounts.
Authy – This app has a different take on the solving the 2-factor authentication issue. In all other apps in this list, once the app is tied with an account the tokens are stored solely on the mobile device housing the app.
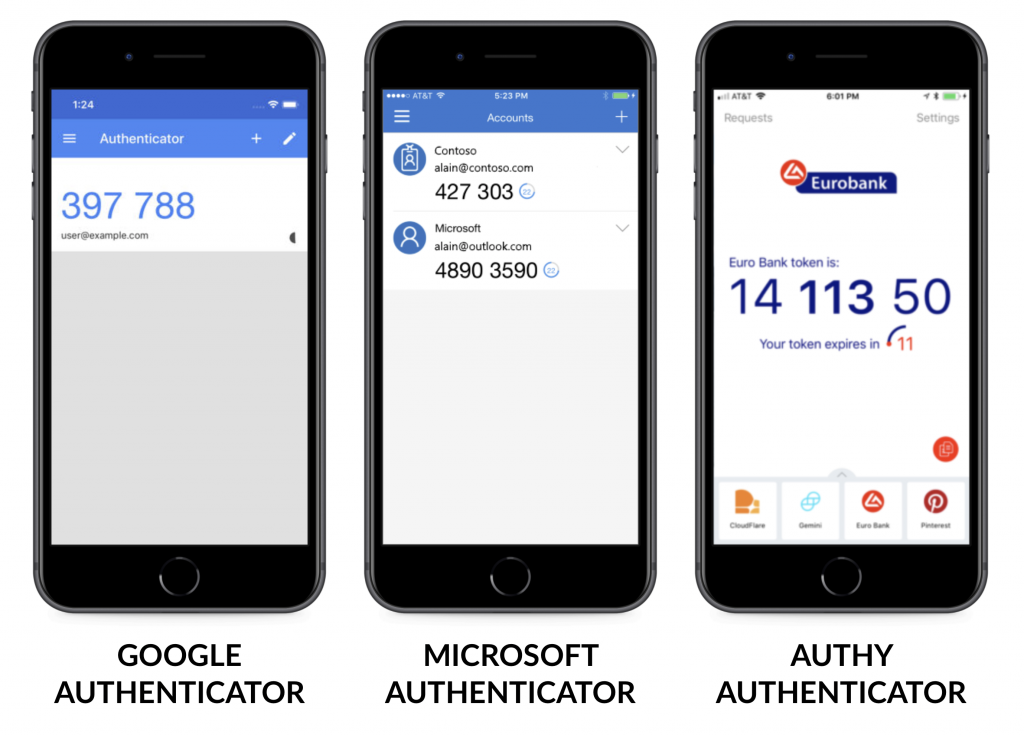
This means if you buy a new phone or lose one you either have to re authenticate every service you use or potentially lose access to your accounts. Authy is based on the cloud, meaning you can use 2-factor authentication on multiple devices.
Physical Authenticators – are small USB devices that look similar to normal pen drives. They work in much the same way as the apps previously mentioned only don’t require codes. The physical keys can be very effective. In 2018 Google reported a complete drop in successful phishing attacks due to use of mandatory keys. Despite this, the keys are very expensive and are not currently widely supported. To see if the service you use are supported visit dongleauth.


